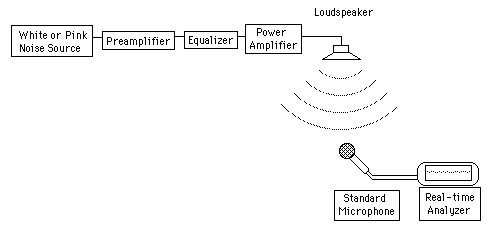
Equalization
One of the most powerful tools for increasing the potential acoustic gain of a sound amplification system is the production of a "mirror image" filter to level the frequency response of the system. The process of equalizing an auditorium also improves the fidelity of the sound. The process of leveling out the frequency response of the sound system removes the peaks which will ring the system before sufficient gain is achieved.
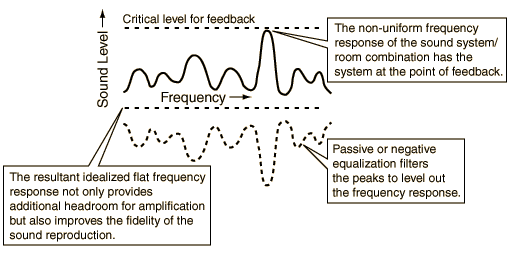
| Ways to increase Potential Acoustic Gain |
Sound reproduction concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |