Non-Stretching Seatbelt
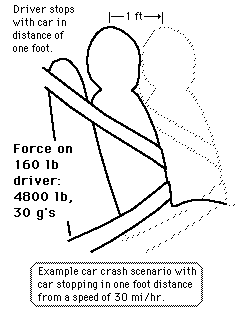 |
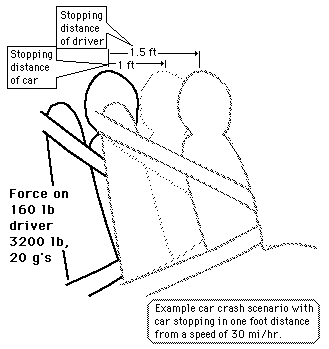
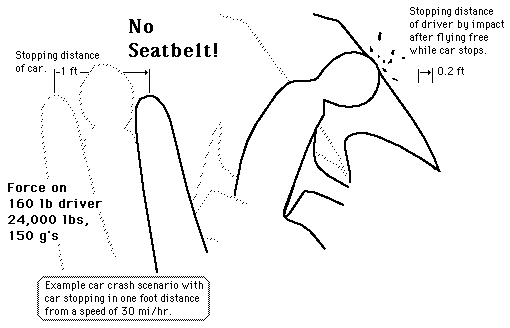
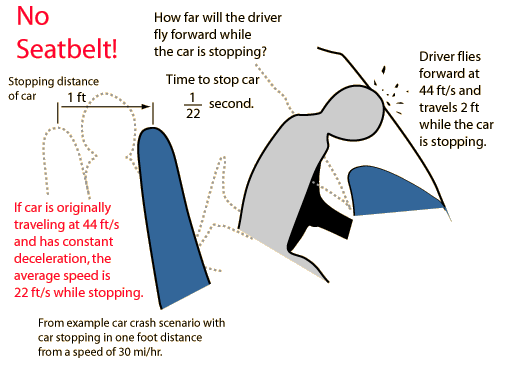
The task of the seatbelt is to stop you with the car so that your stopping distance is probably 4 or 5 times greater than if you had no seatbelt. A crash which stops the car and driver must take away all its kinetic energy, and the work-energy principle then dictates that a longer stopping distance decreases the impact force. For the example car crash scenario the stopping distance is one foot, the force on a 160 lb driver is about 4800 lb or 2.4 tons, and the deceleration about 30 g's. A moderate amount of stretch in the seatbelts will reduce the average impact force. |
Work-energy principle
Car crash scenario
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |