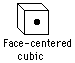
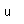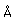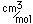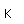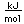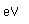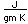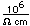Thorium
Thorium is found in nature in the form of the oxide thorite, ThO2 and in the form of thorium phosphate in monazite sand. Thorium is found in the mineral aeschynite.
Thorium has been used in the manufacture of mantles for gas lanterns. The fabric of the mantles is saturated with thorium nitrate and cerium nitrate. The burning of the mantles leaves a residue of thorium and cerium dioxides. This residue glows with a brilliant white luminescence when heated to a high temperature by the gas flame. The presence of the thorium makes these mantles slightly radioactive, so recent mantles have replaced these oxides with other illuminants.
Thorium-232 is one of the small number of isotopes which can be made to undergo nuclear fission, so it could be employed as a nuclear fuel.
|