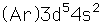Manganese
Manganese is a reactive, silvery-gray metal, with a pinkish tinge. Its principal use is in the manufacture of alloy steel. Manganese steels may have a high percentage of manganese (70-80% manganese, 20-30% iron). These materials are called ferromanganese.
The principal ore of manganese is pyrolusite, MnO2, which occurs in black, massive forms and as a fine black powder. Another form of the oxide MnO2 is called ramsdellite . It also forms an oxide mineral of Mn3O4 called Hausmannite and Mn2O3 in the mineral Bixbyite. Manganese is found in the red mineral rhodochrosite, MnCO3 which is sometimes of gem quality.
Manganese appears in the mineral Bensonite. The hydroxide mineral of manganese is called pyrochroite. Manganese sulfide, MnS, in mineral form is called alabandite. Manganese forms an oxide along with magnesium and other metals in the mineral birnessite. An oxide formed along with barium is called romanechite. Manganese forms an oxide mineral with titanium, iron and lead called senaite. Manganese is a constituent of a number of silicate minerals such as spessartine, Mn3Al2(SiO4)3 and serandite, Na(Mn,Ca)2 Si3O8(OH).
Manganese dioxide is used as an oxidizing agent in ordinary dry cell batteries.
Potassium permanganate, KMnO4, is the most important compound of manganese. Crystallizing as deep red prisms, it dissolves in water to an intensely magenta colored solution. A powerful oxidizing agent, it is used as a disinfectant.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 29 |