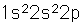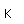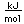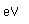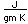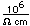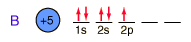Boron
Boron forms brilliant transparent crystals, nearly as hard as diamond. The compound boron carbide, B4C, is the hardest substance known next to diamond. It has found extensive use as an abrasive and for the manufacture of vessels for grinding very hard substances.
Boric acid, H3BO3, is a very weak acid which is used in medicine as a mild antiseptic. Boric acid is a white crystalline solid which is found in nature in some volcanic steam jets in central Italy. It is volatile enough to be carried along by the steam.
Vast deposits of boron are found in California in the form of the minerals borax (sodium tetraborate decahydrate, Na2B4O7. 10H2O), kernite (sodium tetraborate tetrahydrate, Na2B4O7. 4H2O), and colemanite (calcium hexaborate pentahydrate, Ca2B6O11. 5H2O). It is also found in the mineral danburite. It appears with magnesium in the fibrous mineral Szaibelyite and in the mineral boracite.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
|