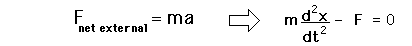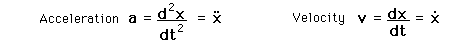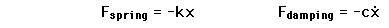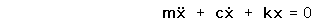Driven Oscillator
If a damped oscillator is driven by an external force, the solution to the motion equation has two parts, a transient and a steady-state part, which must be used together to fit the physical boundary conditions of the problem.

Explanation of motion equation notation
Examples of driven oscillators
| Transient solution | Steady-state solution | Expansion of above terms |
Periodic motion concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |