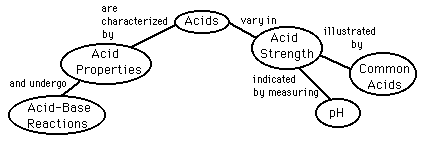
Acids
There are certain acid properties which were noted early in the history of chemistry. According to the Arrhenius acid-base concept, a substance is classified as an acid if it ionizes to form hydrogen(+) ions in aqueous solution. For example, hydrochloric acid reacts with water to form hydrogen ions which are transferred to a water molecule to form a hydronium ion.
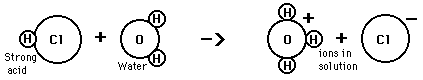
Other systems classify substances as acids if they act as proton donors (Bronsted-Lowry theory) or as electron-pair acceptors (Lewis theory). These two classification methods are not limited to solutions in water.
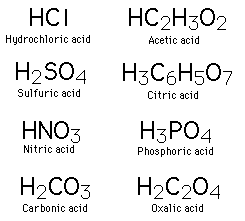
| Common Acids |
| Inorganic Compounds |
Acid Concepts
Chemistry concepts
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |