Sinusoidal Waves
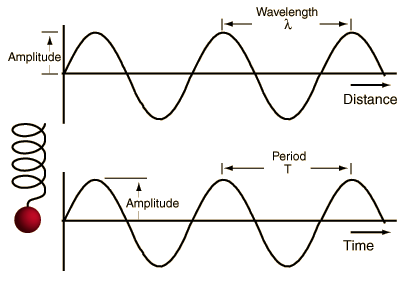 Sine waves can be represented mathematically and it can be shown that any wave can be constructed from an appropriate combination of sine waves (Fourier synthesis) |
Any single- frequency traveling wave will take the form of a sine wave. This transverse wave is typical of that caused by a small pebble dropped into a still pool. The position of an object vibrating in simple harmonic motion will trace out a sine wave as a function of time. (Or if a mass on a spring is carried at constant speed across a room, it will trace out a sine wave.) |
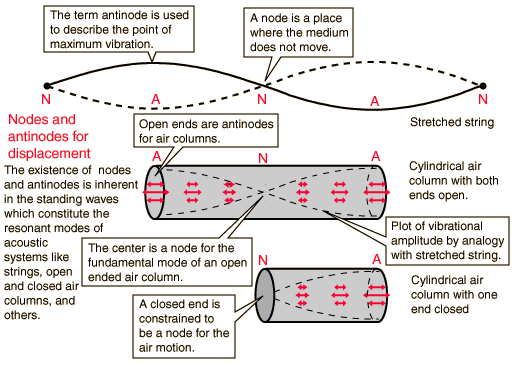
Wave concepts
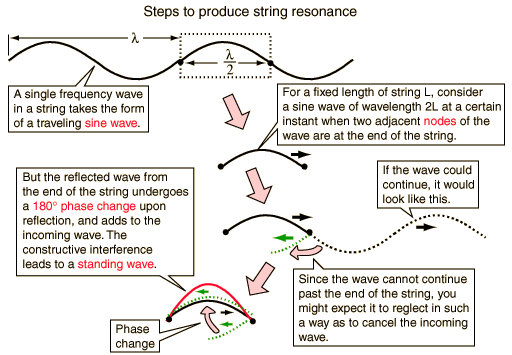
Resonance concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |