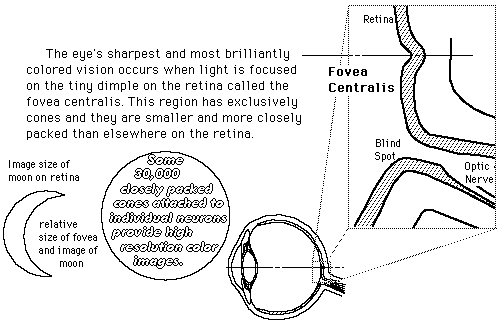
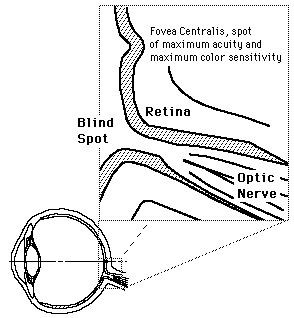
The Retina
The retina is a light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that covers about 65 percent of its interior surface. Photosensitive cells called rods and cones in the retina convert incident light energy into signals that are carried to the brain by the optic nerve. In the middle of the retina is a small dimple called the fovea or fovea centralis. It is the center of the eye's sharpest vision and the location of most color perception.
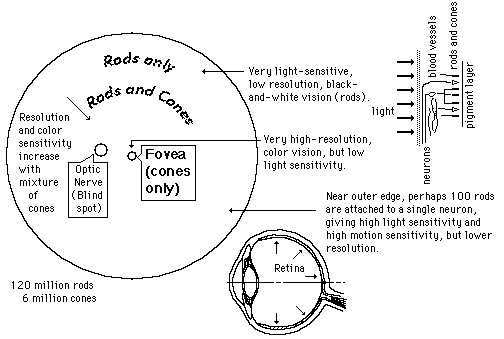
"A thin layer (about 0.5 to 0.1mm thick) of light receptor cells covers the inner surface of the choroid. The focused beam of light is absorbed via electrochemical reaction in this pinkish multilayered structure. The human eye contains two kinds of photoreceptor cells; rods and cones. Roughly 125 million of them are intermingled nonuniformly over the retina. The ensemble of rods(each about 0.002 mm in diameter in some respects has the characteristics of a high-speed, black and white film(such as Tri-X). It is exceedingly sensitive, performing in light too dim for the cones to respond to, yet it is unable to distinquish color, and the images it relays are not well defined."(Hecht)
"In contrast, the ensemble of 6 or 7 million cones (each about 0.006 mm in diameter) can be imagined as a separate, but overlapping, low-speed color film. It performs in bright light, giving detailed colored views, but is fairly insensitive at low light levels."(Hecht)"
Vision concepts
Image formation concepts
Reference
Hecht, 2nd Ed.
Sec. 5.7
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |