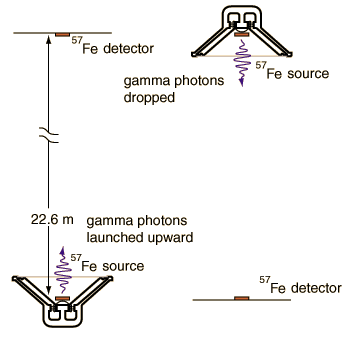
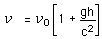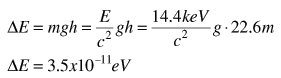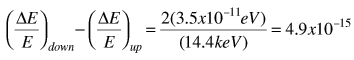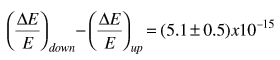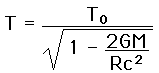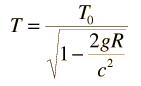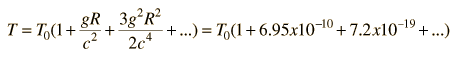Harvard Tower Experiment
 |
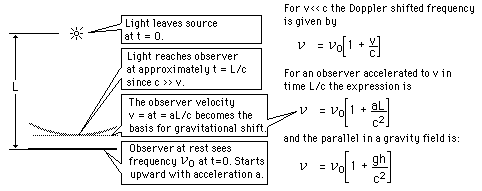
In just 22.6 meters, the fractional gravitational red shift given by
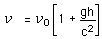 is just 4.92 x 10^-15 , but the Mossbauer effect with the 14.4 keV gamma ray from iron-57 has a high enough resolution to detect that difference. In the early 60's physicists Pound, Rebka,and Snyder at the Jefferson Physical Laboratory at Harvard measured the shift to within 1% of the predicted shift.
is just 4.92 x 10^-15 , but the Mossbauer effect with the 14.4 keV gamma ray from iron-57 has a high enough resolution to detect that difference. In the early 60's physicists Pound, Rebka,and Snyder at the Jefferson Physical Laboratory at Harvard measured the shift to within 1% of the predicted shift.
|
By just using the expression for gravitational potential energy near the Earth, and using the m in the relativistic energy expression, the gain in energy for a photon which falls distance h is
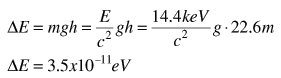
Comparing the energy shifts on the upward and downward paths gives a predicted difference
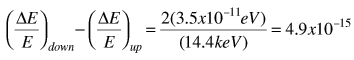
The measured difference was
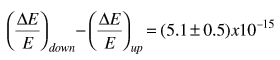
The success of this experiment owed much to the care of Pound and Rebka in preparing the source. They electroplated cobalt-57 onto the surface of a thin sheet of iron and then heated the combination at 1220 K for an hour. The heat treatment caused the cobalt to diffuse into the iron to a depth of about 300 nm or 1000 atomic spacings. The source was then mounted on the cone of a loudspeaker driven at 10Hz to sweep the source velocity in a sinusoidal variation. The detector was a thin sheet of iron about 14 micrometers thick which was also annealed. The heat treatments were found to be crucial in obtaining high resolution.
|
Index
General relativity ideas
References |