Polarization by Reflection
Since the reflection coefficient for light which has electric field parallel to the plane of incidence goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is partially polarized.
From Fresnel's equations it can be determined that the parallel reflection coefficient is zero when the incident and transmitted angles sum to 90°. The use of Snell's law gives an expression for the Brewster angle.
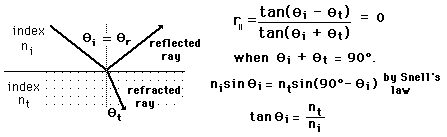
| More detail on: | Polarization by reflection | Calculation of partial polarization |
Reflection concepts
Incident light behavior
Polarization concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |