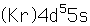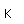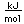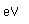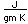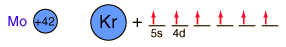Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a metal which has important use as a constituent of alloy steels.
It is found principally in the mineral molybdenite, MoS2, of which there is an enormous deposit near Climax, Colorado. The mineral forms in shiny black plates, similar to graphite in appearance. Other mineral forms are Powellite and Wulfenite.
Molybdenum is an exception to the general order of filling of electron orbitals like chromium in the previous period of the same column of the periodic table. It fills five 4d states before it fills the second 5s state. Just those levels outside a krypton core are shown.
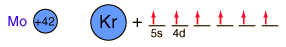
|