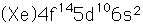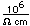Mercury
Mercury is the only metal which is liquid at room temperature. Two others melt close to room temperature (cesium at 28.5°C and gallium at 29.8°C). Because of its unreactivity, fluidity, high density, and high electrical conductivity, it finds many uses in scientific apparatus. Thermometers, barometers, and thermostats are common applications.
Alloys of mercury are called amalgams. Amalgams of silver, gold and tin are used in dentistry.
Mercury does not wet iron, and it is typically shipped in iron flasks.
Mercury forms an oxide mineral called Montroydite.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 28 |