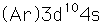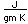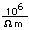Copper
Copper is a red, tough metal with a moderately high melting point. It is an excellent conductor of heat and of electricity and finds extensive use as an electric conductor.
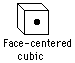
Pure copper is soft and can be drawn into wire or hammered into desired shapes. These shaping processes cause the metal to become hard because the large crystal grains are broken into smaller grains, strengthening the metal. If the copper is subsequently heated (annealed), it can be made soft again.
Copper and zinc are alloyed to make brass, and alloyed with tin to make bronze. Alloys of copper and aluminum are called aluminum bronze.
Copper sulfate (CuSO4.5H20) is a common compound of copper. Copper sulfate is used in copper plating, in fabric printing, and in electric cells. Common names are blue vitriol and blustone. Copper appears in nature in a variety of mineral forms. It appears with magnesium in the carbonate mineral Callaghanite. Cuprite is the mineral form of the oxide CuO. Copper forms an oxide with iron called delafossite. Copper forms the sulfides chalcocite, Cu2S, and digenite, Cu9S5. With iron it forms chalcopyrite, CuFeS2 and with antimony it forms chalcostibite, CuSbS2. Copper also forms a sulfide with bismuth called emplectite, CuBiS2. It forms a sulfide with antimony and iron called tetrahedrite.
Sulfides with iron include bornite, Cu5FeS4, and cubanite, CuFe2S3. A sulfide with arsenic is called enargite. Bournonite is a sulfide with copper, lead and antimony. Tennantite is a sulfide which contains copper, arsenic, iron and antimony. Lead, copper and iron join in the sulfide betekhtinite. Copper, cobalt and nickel join in the sulfide carrollite. A striking green color is exhibited by the mineral bayldonite which combines copper, zinc and lead with an arsenate group. Another green copper mineral is the copper arsenate olivenite, Cu2AsO4(OH).
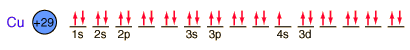
Copper is one of the few exceptions to the general order of filling of electron orbitals, filling all ten 3d states before it fills the second 4s state.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 28 |