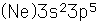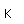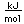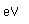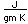Chlorine
Chlorine is the most common of the halogens. It is not as chemically active as fluorine, but is still very active and forms compounds with most elements. In pure form, it is a greenish-yellow gas with a sharp, irritating odor. It is manufactured on a large scale by electrolysis of concentrated solutions of sodium chloride.
Chlorine is a strong oxidizing agent and as a result is effective in killing bacteria. This has led to widespread use in the sterilization of drinking water, for swimming pools, etc.
Hydrogen chloride, HCl, is a gas with a sharp unpleasant odor. The gas dissolves readily in water with the liberation of heat. This forms hydrochloric acid, a very strong acid.
Chlorine is a constituent of many mineral crystals. From simple clear ionic crystals like halite, NaCl, to more complex halide containing minerals like the yellow crystals of mimetite, Pb5(AsO4)3Cl, chlorides show a range of colors.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 13 |