Electron-Positron Annihilation Provides Evidence of Three Colors for Quarks
One of the definitive experiments which supports the quark model is the high energy annihilation of electrons and positrons. The annihilation can produce muon-antimuon pairs or quark-antiquark pairs which in turn produce hadrons. The hadron events are evidence of quark production. The ratio of the number of hadron events to the number of muon events gives a measure of the number of "colors" of the quarks, and the evidence points to five quarks with three colors. With the more recent evidence for the top quark, these experiments provide support for the standard model of six quarks with three colors.
The models which are evoked to explain the experimental results illustrated below involve the calculated cross-sections for the scattering events. It is helpful that the same type of scattering events, i.e., electron-positron scattering, can yield either two muons (leptons) or a variety of hadron products, any one of which suggests the creation of quarks. The experimental handle is then the relative frequency of the hadron events compared to the muon events. The calculated ratio of the products is the ratio of the cross-sections, and this ratio depends upon the ratio of the squares of the electric charges of the products. The calculated ratio then depends upon the number of types of quark-antiquark pairs which can be produced. So it has the form
If we use the five quarks which would be available in this energy regime, the u, d, s, c and b quarks, then we get
which is obviously wrong compared to the experiment. But when we take into account the three colors, we obtain
This produces good agreement with the experimental observations over a wide range of energy when the quantum chromodynamic corrections are applied. Obviously, there is a great deal which is not being said here about the details of the calculations. But hopefully it can be seen that this kind of experimental evidence is a strong check on the standard quark model. It includes the model's charges of 2e/3 and e/3, the five types of quarks, and the three colors.
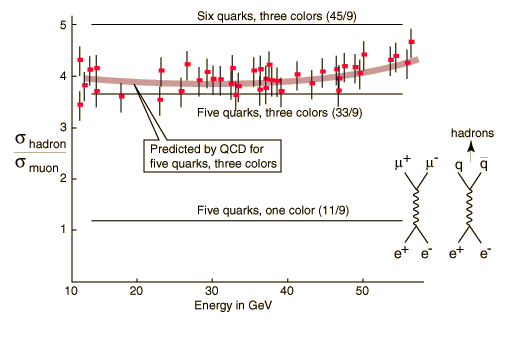
The sixth quark is not seen because the energies used are not sufficient to produce the top-antitop quark pair.
Particle concepts
Reference
Rohlf
Ch. 18