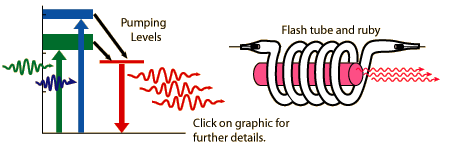
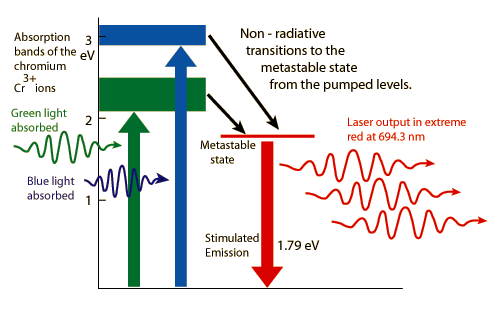
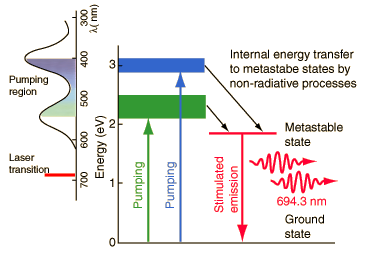
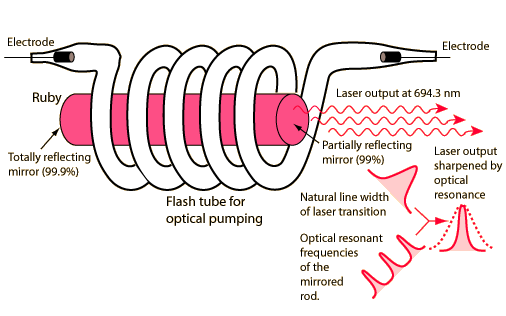
Neodymium-YAG Laser
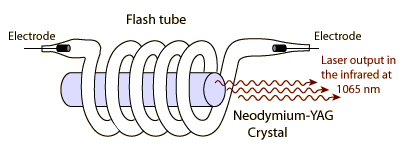
An example of a solid-state laser, the neodymium-YAG uses the Nd3+ ion to dope the yttrium-aluminum-garnet (YAG) host crystal to produce the triplet geometry which makes population inversion possible. Neodymium-YAG lasers have become very important because they can be used to produce high powers. Such lasers have been constructed to produce over a kilowatt of continuous laser power at 1065 nm and can achieve extremely high powers in a pulsed mode.
Neodymium-YAG lasers are used in pulse mode in laser oscillators for the production of a series of very short pulses for research with femtosecond time resolution.
Laser concepts
Laser types
Reference
Boraiko
| HyperPhysics***** Quantum Physics ***** Optics | R Nave |