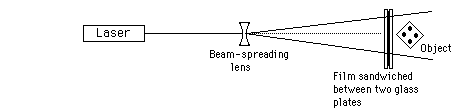
Hologram History
Historical notes:
Gabor was the discoverer of the hologram and received the Nobel Prize in Physics for it in 1971. This was pre-laser holography of course, and he made holograms only of transparencies where his reference beam was the unobstructed light which went through the clear parts of the transparency.
Leith and Upatnieks developed the off-axis reference beam method which is most often used today. It permitted the making of holograms of solid objects by reflected light.
Denisyuk contributed to the development by using Lippmann's photographic process to make reflection holograms which could be viewed in color if more than one coherent source was available. In his method the beam was passed through the photographic emulsion and back reflected from the object. The emulsion could then be mounted on a reflective backing for viewing by reflected light.
Benton is credited with the development of the rainbow hologram. Since it can be mass-copied and viewed with incoherent white light, it has become the most common type of hologram. Rainbow holograms have appeared on National Geographic's cover and on millions of credit cards as a deterrent to counterfeiting.
Composite holograms are made as multiple strips so that you get a different image from different angles. They can be viewed in white light.
|