| Radiation units |

|
Index | |
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Meet the Millirem
|
Index Radiation exposure examples Reference Cohen, Bernard | ||
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Meet the MilliremThe risk of one millirem of radiation dose is a 1 in 8 million risk of dying of cancer if large dose effects extrapolate linearly to zero dose. The loss in life expectancy from a 1 millirem dose is about 1.2 minutes, equivalent to:
|
Index Radiation exposure examples Reference Cohen, Bernard | ||
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Typical Radiation Doses in Millirem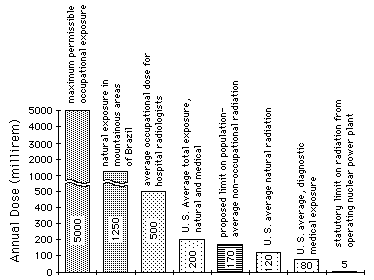
|
Index Radiation exposure examples Reference Nave & Nave, 3rd Ed. | |
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Environmental Radiation ExposureU.S. Average Exposure
Note: This does not include radon exposures, which may be very high.
|
Index Radiation exposure examples Reference Bushong | |||||||||||||
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Press Overreaction to Radiation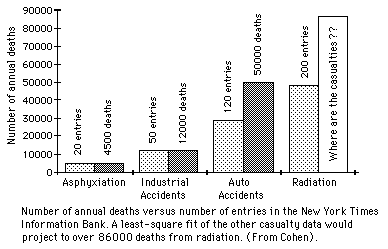 When it became evident in the 70's and 80's that radon exposure in one's own home is probably greater than the radiation exposures which had regularly been trumpeted in headlines, we entered another awkward era in the reporting of radiation issues.
|
Index Radiation exposure examples Reference Cohen | |
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Acute Radiation ExposureEffects of Large, Whole-Body Radiation Doses
|
Index Radiation exposure examples Reference Nave & Nave | |||||||||||||
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Increased Cancer Risk:Bomb Victims
|
Index Radiation exposure examples | |||
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Hiroshima and Nagasaki RadiationThe Nagasaki bomb was an "implosion" device with high explosive wrapped around the plutonium. The violent compression detonated the plutonium, but also absorbed a considerable fraction of the neutrons so that the main flux from the blast was gamma rays. The Hiroshima bomb was a uranium bomb of the gun type and, having no neutron capturing shroud, it produced a much higher neutron flux. There were 140,000 fatalities within four months in Hiroshima and 70,000 in Nagasaki. A 1986 study estimated the neutron dose at 1000 meters from ground zero Hiroshima was 1% of total dose but 15-20% of radiation sickness. New studies of concrete with an accelerator mass spectrometer which measured the chlorine-36 isotope indicate a neutron flux 10 times higher. The gamma doses were estimated by thermoluminescent dosimetry of roof tiles in the blast areas, but no such test existed for the neutron measurement.
|
Index Radiation exposure examples | |
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |
Correlation between smoking and lung cancer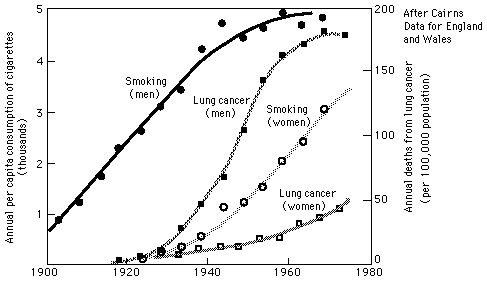 John Cairns, The Cancer Problem, Scientific American 233, Nov 1975, p64 |
Index Radiation exposure examples |
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | Go Back |