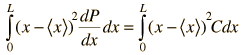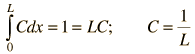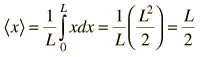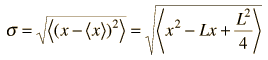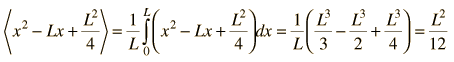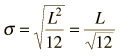The Standard Deviation
The root-mean-square deviation of x from its average is called the standard deviation. For a set of discrete measurements, the standard deviation takes the form
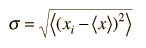 | for discrete measurements of x |
and
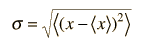 | for continuous x where < > implies average. |
Determining the average or mean in the above expression involves the distribution function for the variable.
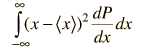
| Example of free particle in a box |
Applied statistics concepts