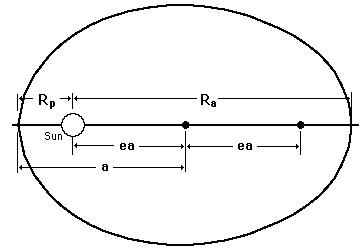
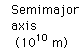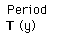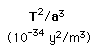The Law of Orbits
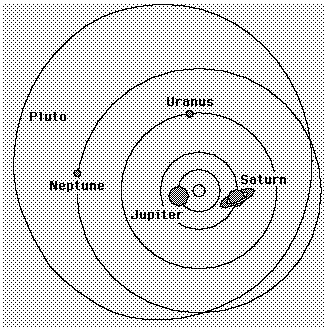
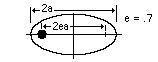
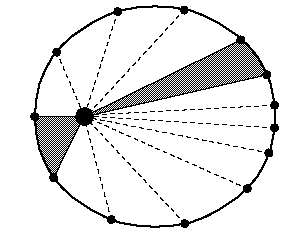
All planets move in elliptical orbits, with the sun at one focus.
|
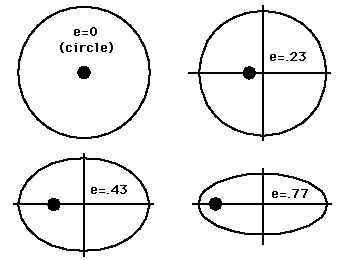
This is one of Kepler's laws. The elliptical shape of the orbit is a result of the inverse square force of gravity. The eccentricity of the ellipse is greatly exaggerated here. 
|
Gravity concepts
Orbit concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |